Results
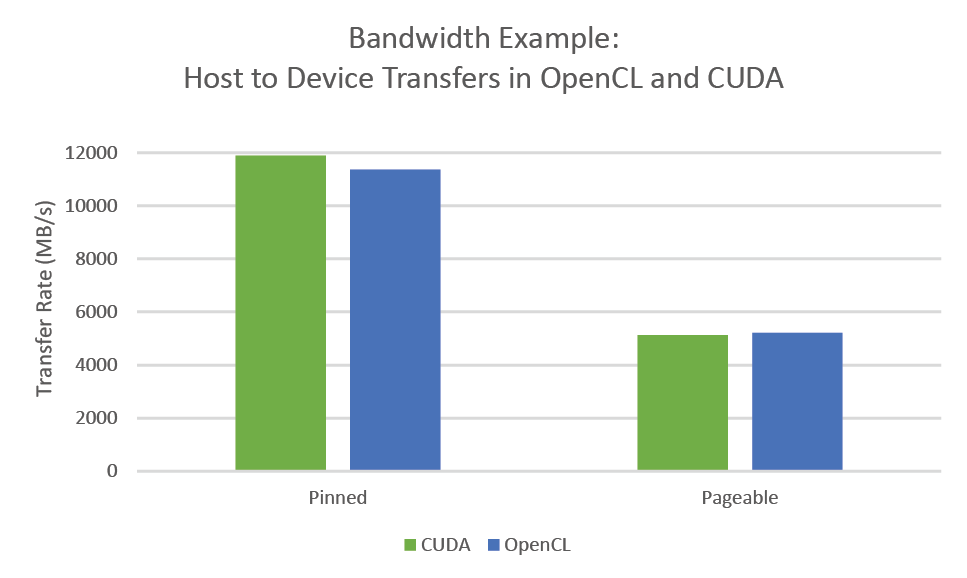
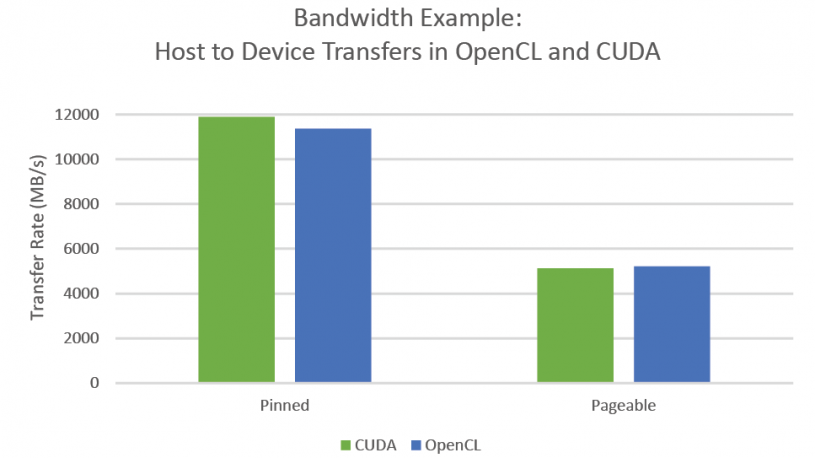
The NVIDIA CUDA Bandwidth example discussed before has an OpenCL equivalent available here (the OpenCL examples had previously been removed from the CUDA SDK, much to some people’s chagrin). A basic comparison was made to the OpenCL Bandwidth test downloaded 12/29/2015 and the CUDA 7.5 Example Bandwidth Test provided in with the CUDA SDK. Interestingly, the OpenCL bandwidth runs in PAGEABLE mode by default while the CUDA example runs in PINNED mode and resulting in an apparent doubling of speed by moving from OpenCL to CUDA. However, the OpenCL bandwidth example also has a PINNED memory mode through the use of mapped buffer transfers and we find that OpenCL and CUDA operate comparably.
Operation
The OpenCL example runs in either PINNED or PAGEABLE mode, where PAGEABLE corresponds to standard clEnqueueWriteBuffer commands and PINNED mode corresponds to an equivalent and faster clEnqueueMapBuffer and subsequent clEnqueueWriteBuffer to perform the transfer.
if(memMode == PINNED)
{
// Get a mapped pointer
h_data = (unsigned char*)clEnqueueMapBuffer(cqCommandQueue, cmPinnedData, CL_TRUE, CL_MAP_READ, 0, memSize, 0, NULL, NULL, &ciErrNum);
oclCheckError(ciErrNum, CL_SUCCESS);
} // DIRECT: API access to device buffer
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < MEMCOPY_ITERATIONS; i++)
{
ciErrNum = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(cqCommandQueue, cmDevData, CL_FALSE, 0, memSize, h_data, 0, NULL, NULL);
oclCheckError(ciErrNum, CL_SUCCESS);
}
ciErrNum = clFinish(cqCommandQueue);
oclCheckError(ciErrNum, CL_SUCCESS);</pre>
<pre> //get the the elapsed time in seconds
elapsedTimeInSec = shrDeltaT(0);
//calculate bandwidth in MB/s
bandwidthInMBs = ((double)memSize * (double)MEMCOPY_ITERATIONS)/(elapsedTimeInSec * (double)(1 << 20));
//clean up memory
if(cmDevData)clReleaseMemObject(cmDevData);
if(cmPinnedData)
{
clEnqueueUnmapMemObject(cqCommandQueue, cmPinnedData, (void*)h_data, 0, NULL, NULL);
clReleaseMemObject(cmPinnedData);
}
OpenCL Example Run
Running on... GeForce GTX 750 Quick Mode Host to Device Bandwidth, 1 Device(s), Paged memory, direct access Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 5125.9 Device to Host Bandwidth, 1 Device(s), Paged memory, direct access Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 5181.6 Device to Device Bandwidth, 1 Device(s) Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 64039.2 [oclBandwidthTest.exe] test results... PASSED
CUDA Example Run
[CUDA Bandwidth Test] - Starting... Running on... Device 0: GeForce GTX 750 Quick Mode Host to Device Bandwidth, 1 Device(s) PINNED Memory Transfers Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 11888.0 Device to Host Bandwidth, 1 Device(s) PINNED Memory Transfers Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 11948.6 Device to Device Bandwidth, 1 Device(s) PINNED Memory Transfers Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(MB/s) 33554432 68545.4 Result = PASS